One of the aims of the REPAiR project was to develop, test and apply a geodesign decision support environment (GDSE). The GDSE is an online tool designed for workshop sessions where small groups of participants cooperatively develop strategies for a more circular economy with a special focus on waste and resource management.
In the REPAiR project the Peri-Urban Living Labs (PULL) provided these workshop series in which the GDSE was applied. The GDSE can also be used for workshop settings and research questions outside of the REPAiR project. It is designed as an open source tool. Therefore, it can be used free of charge. If necessary, it can also be modified by future users in order to meet their individual project needs.
Following the overall idea of a collaborative process of strategy development (“co-design”), the GDSE guides its users through five steps:
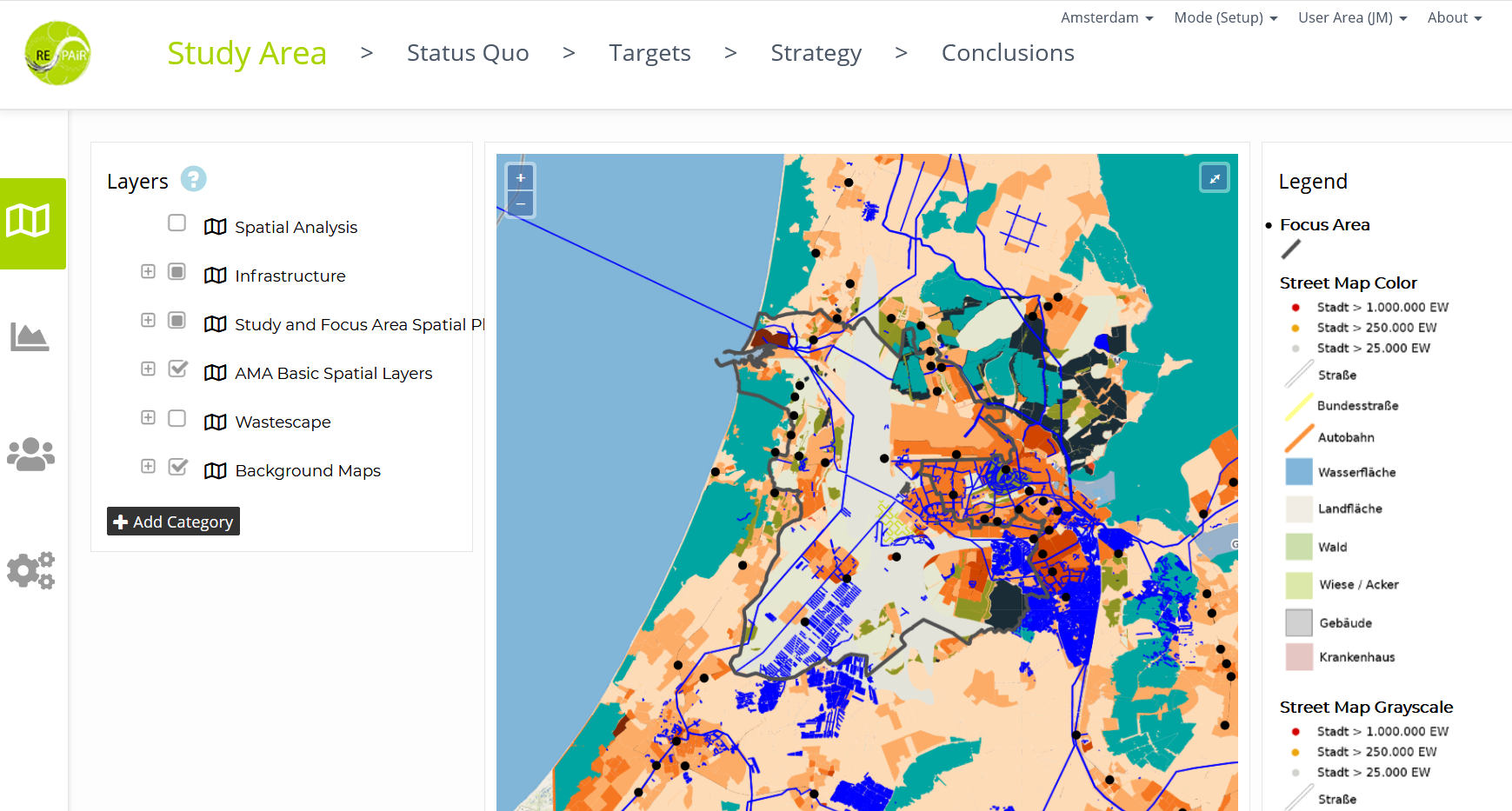
- Study Area
- Status Quo
- Targets
- Strategy
- Conclusions
These five steps are always visible in the GDSE’s top menu.

In the first step, the users can define their study area using external map services as well as individual layer files, e.g. containing their data collection on the status quo situation and upcoming future developments. In addition, the key flows are defined, on which the workshops or the research activity using the GDSE are focusing on. This includes defining the relevant stakeholders.
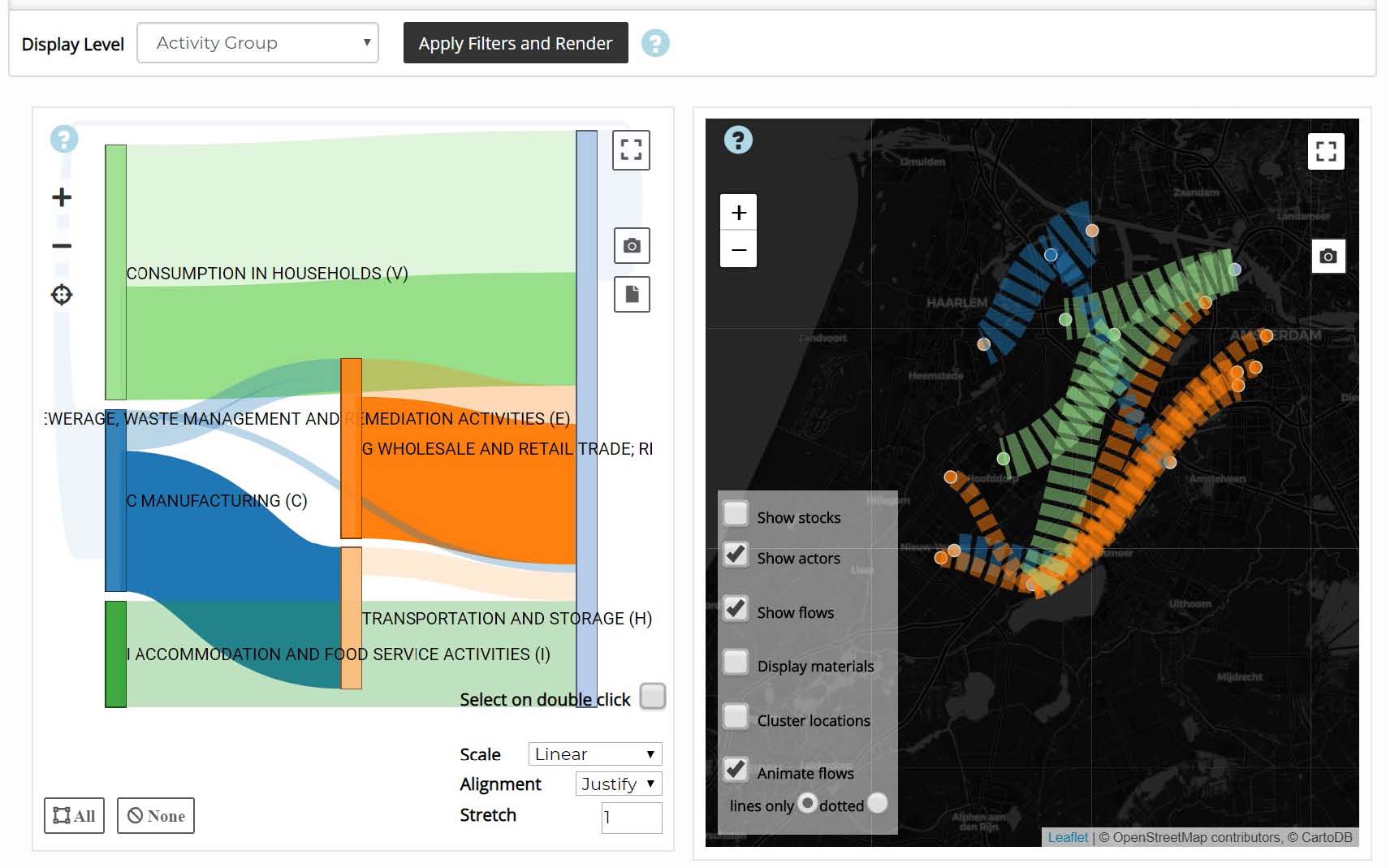
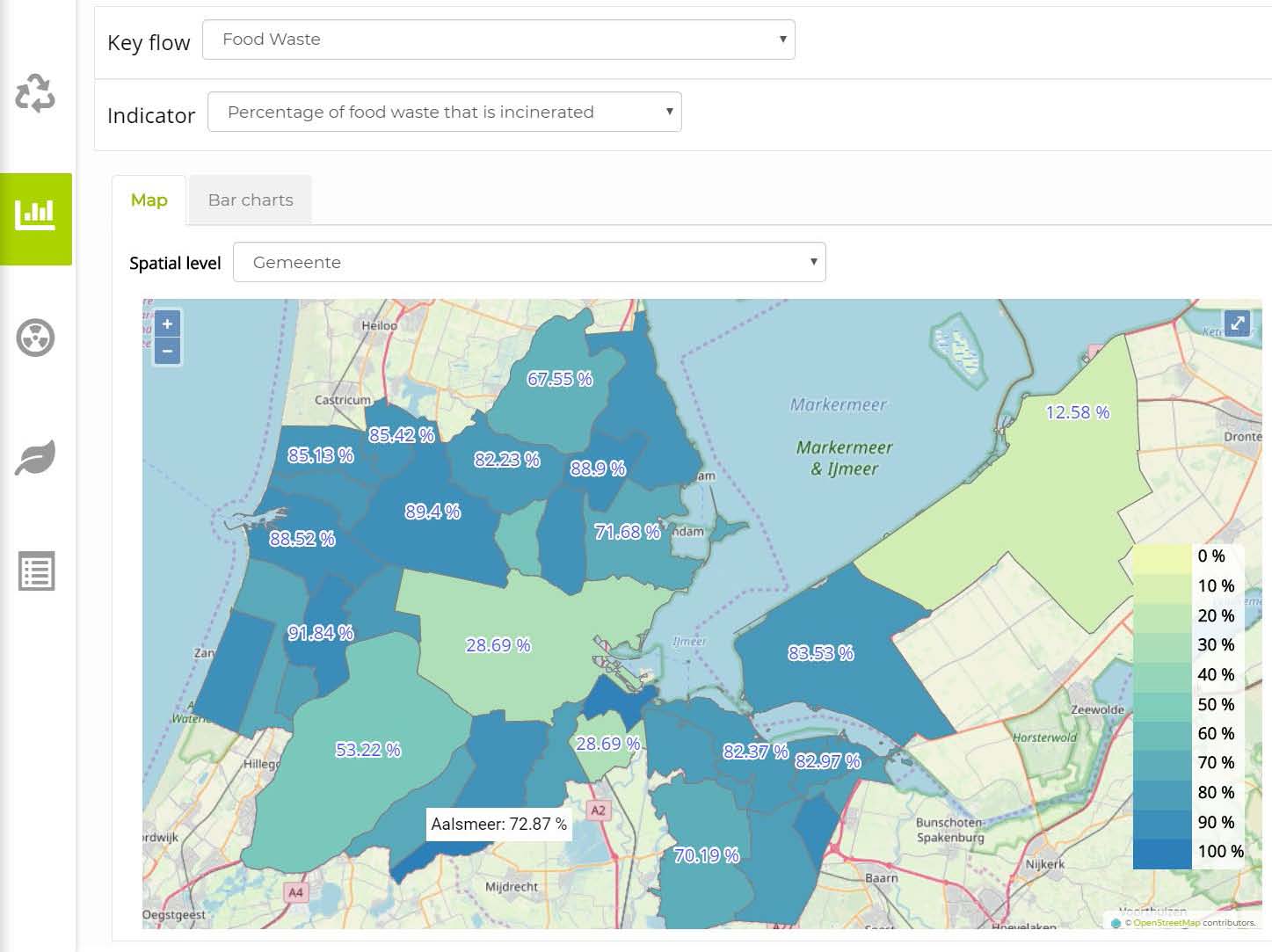
Step two of the GDSE is called “Status quo” and takes a detailed look on the status quo situation of the material and waste flows between the different activities in the study area. It also looks on the flows going into the study area or leaving it for other regions, countries or parts of the world.
The GDSE allows to visualise the flows using classic Sankey diagrams as well as map representations. The ability to visualise the data and outcomes of an activity-based spatial material flow analysis (ASMFA) on different levels of aggregation was one of the major goals of the GDSE development. All these visualisations help the workshop users to explore the status quo situation, evaluate its short-comings and develop ideas for future improvements.
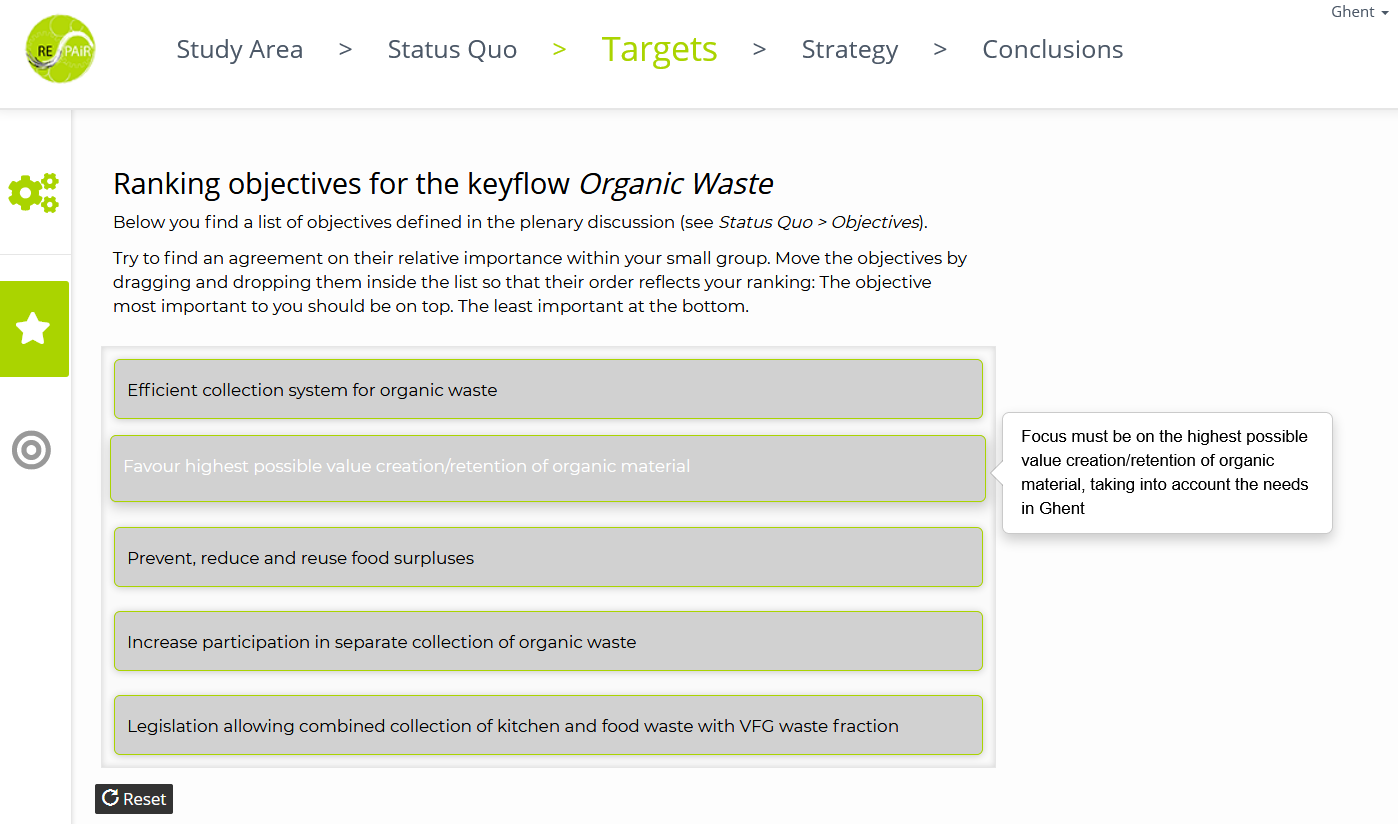
The work with small groups within the workshop setting starts with the third step of the GDSE, titled “Targets”. Here, each small group ranks overall objectives (taken from earlier workshops without the GDSE) for the later strategy developments and transforms them into mostly quantitative targets (e.g. “reduction of non-recycled organic household waste by 30%”).
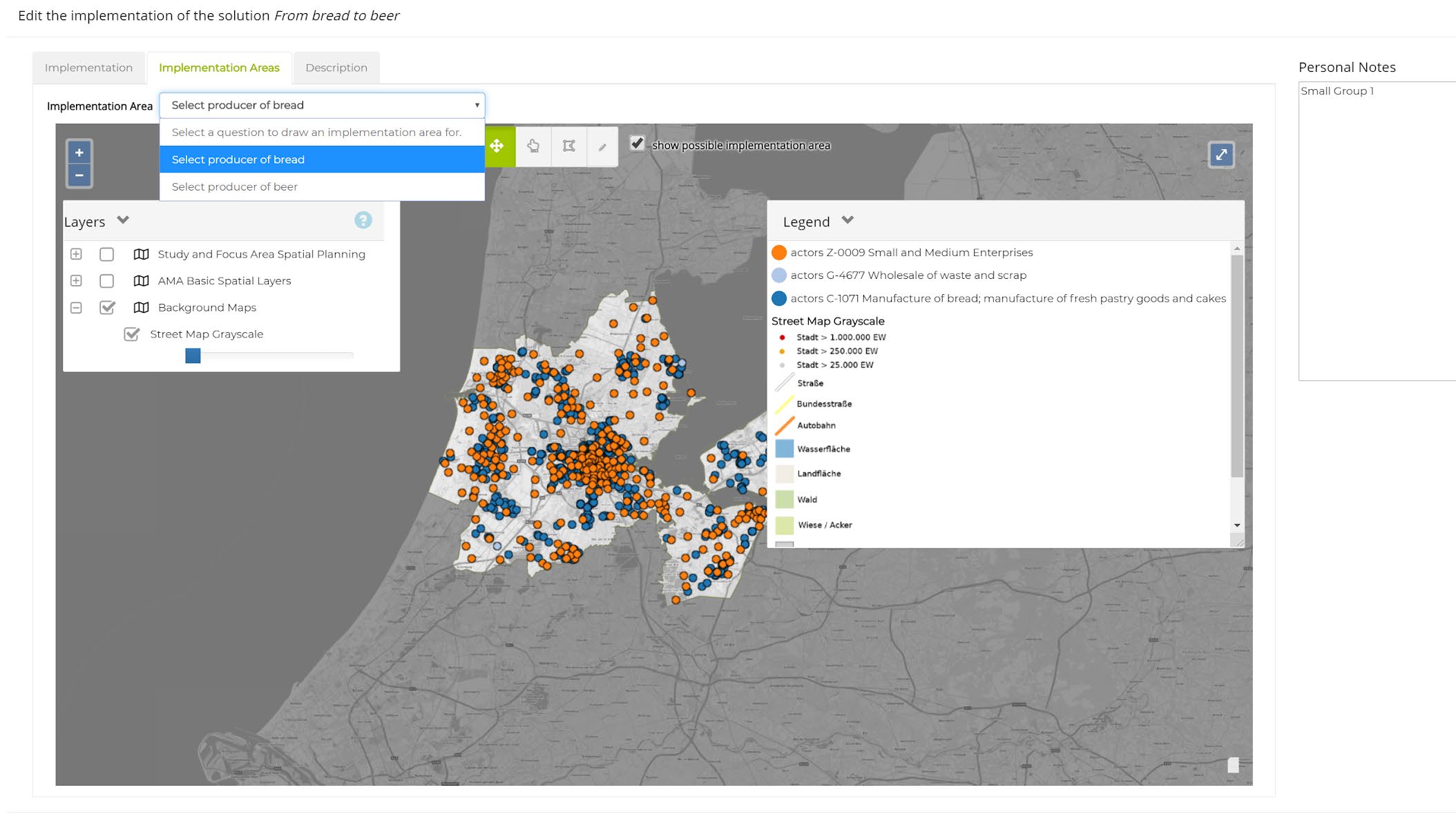
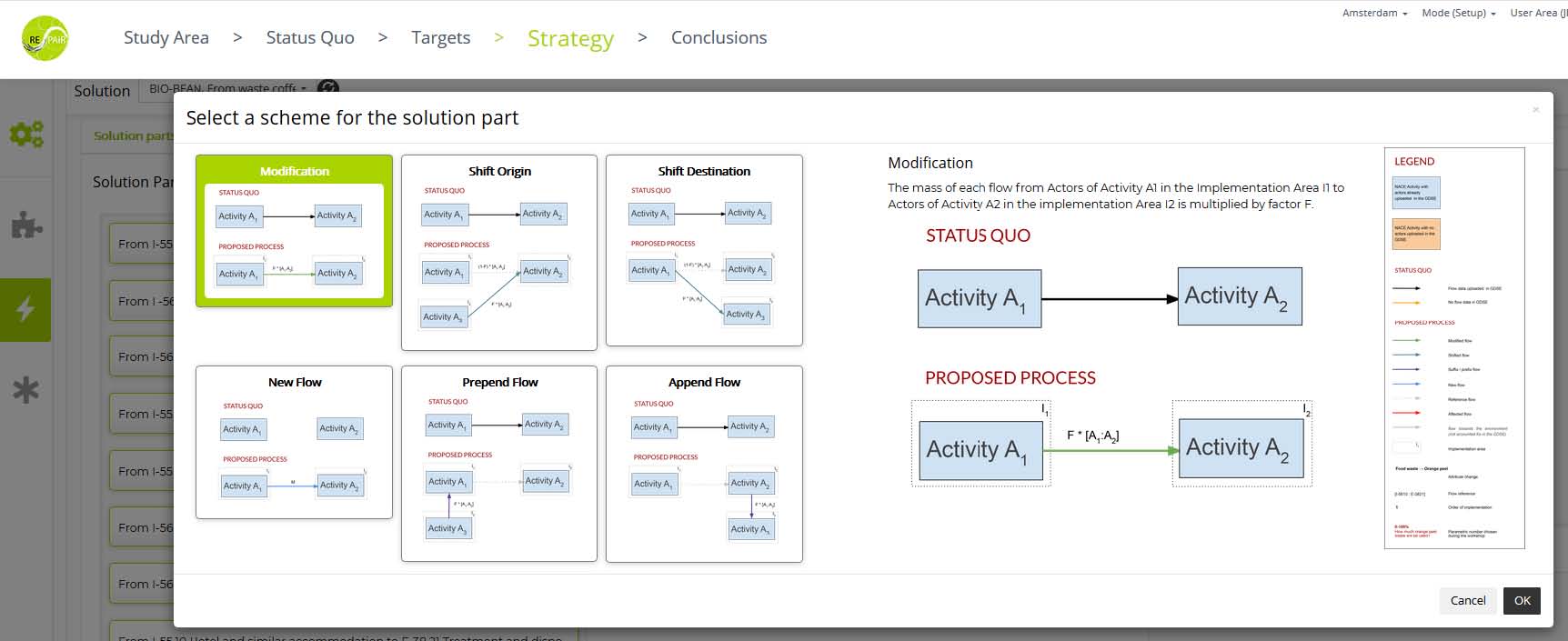
In the next step, each small group is asked to put together a Strategy aiming to reach the objectives and targets set in the step before. In the GDSE-terminology, a “strategy” is a combination of solutions implemented in a specific area by specific stakeholders. The workshop users pick solutions from a predefined catalogue and implement them within the study area.
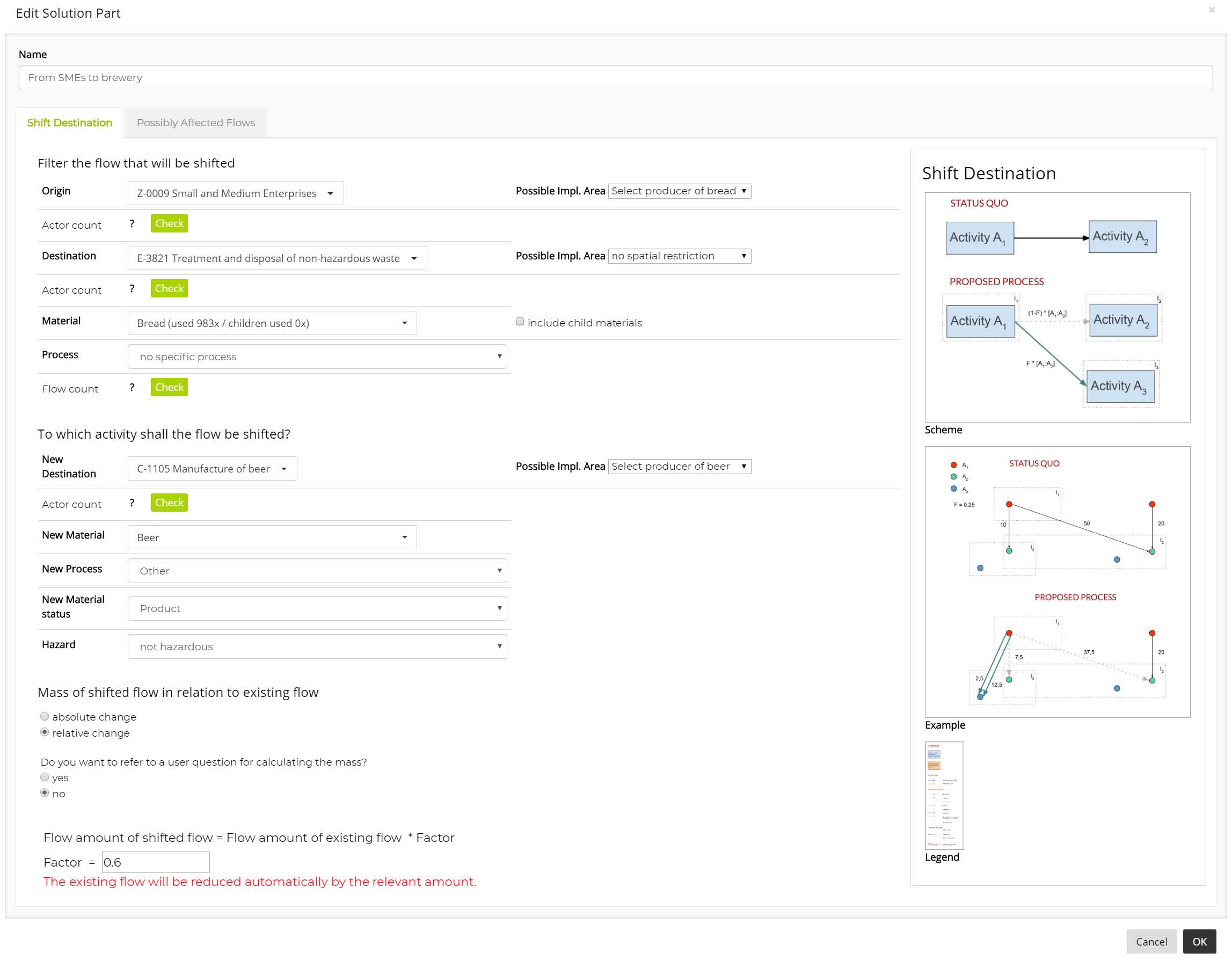
When setting up the catalogue of solution for a workshop, the organising team of planners or researchers defines each solution by describing how it will modify the existing flows when implemented in an area.
The GDSE uses these definitions to estimate the effects of the selected solutions on the status quo flows. For enabling the GDSE algorithm to do so, the workshop team can use a detailed description technique implemented in the GDSE’s setup mode not visible to the later workshop users.
After putting together a strategy, each small group can start the calculation of its possible effects on the waste and material flows in the study area. By comparing to changes already achieved by the strategy with the own targets set earlier, each small group has the chance to redesign its strategies by changing the selected solutions or modifying their implementation area and settings.
After putting together a strategy, each small group can start the calculation of its possible effects on the waste and material flows in the study area. By comparing to changes already achieved by the strategy with the own targets set earlier, each small group has the chance to redesign its strategies by changing the selected solutions or modifying their implementation area and settings.
The last step of the GDSE brings back together the small groups in a plenum setting and helps to draw conclusions from the results of the different small groups. It does this by commonly leading the workshop participants through a 9-step-evaluation asking the following questions.
- How were the objectives ranked by the small groups?
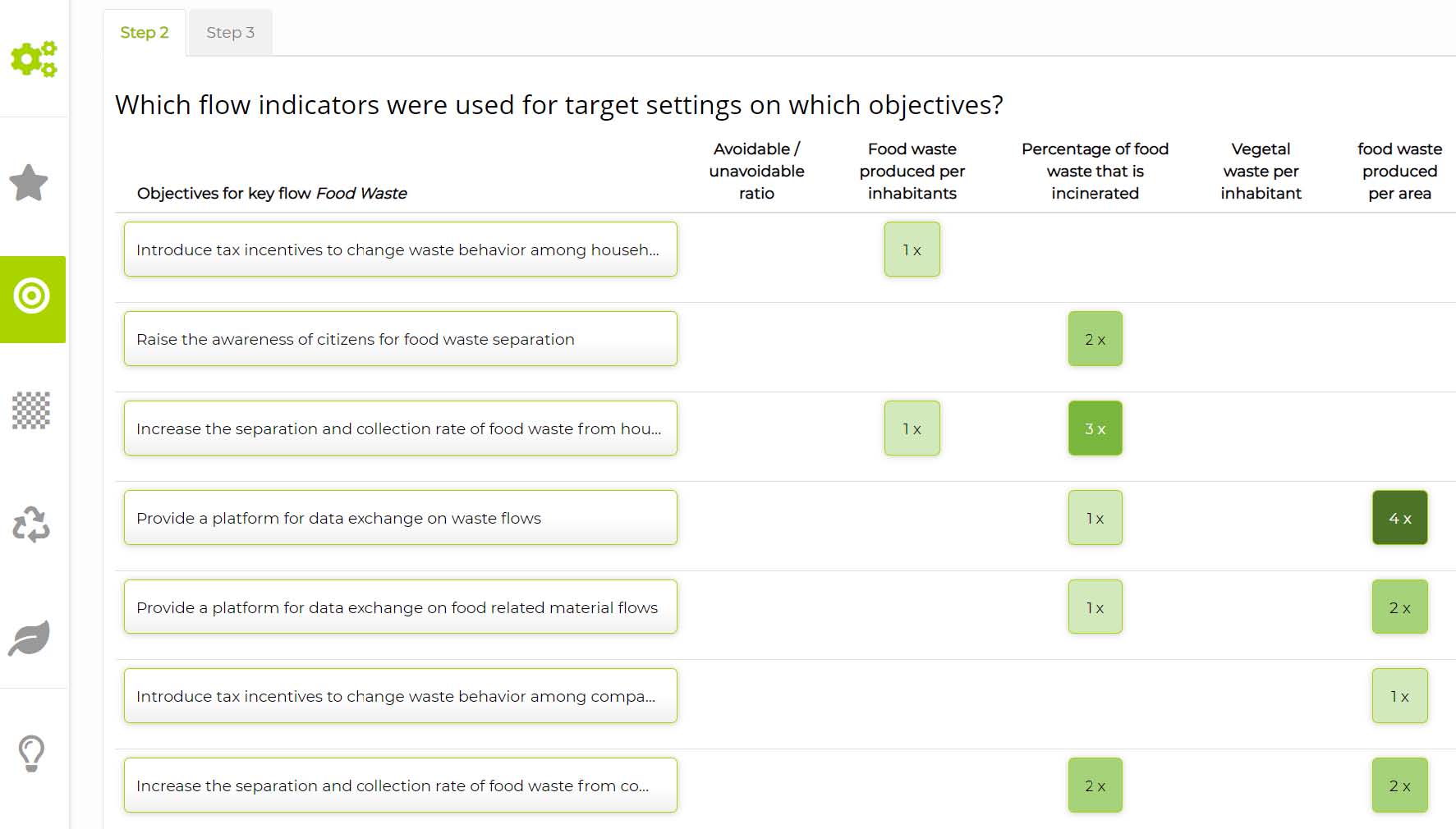
- Which flow indicators were used for target settings on which objectives?
- Which target values were set?
- Which solutions were selected for the strategies? How where the questions answered?
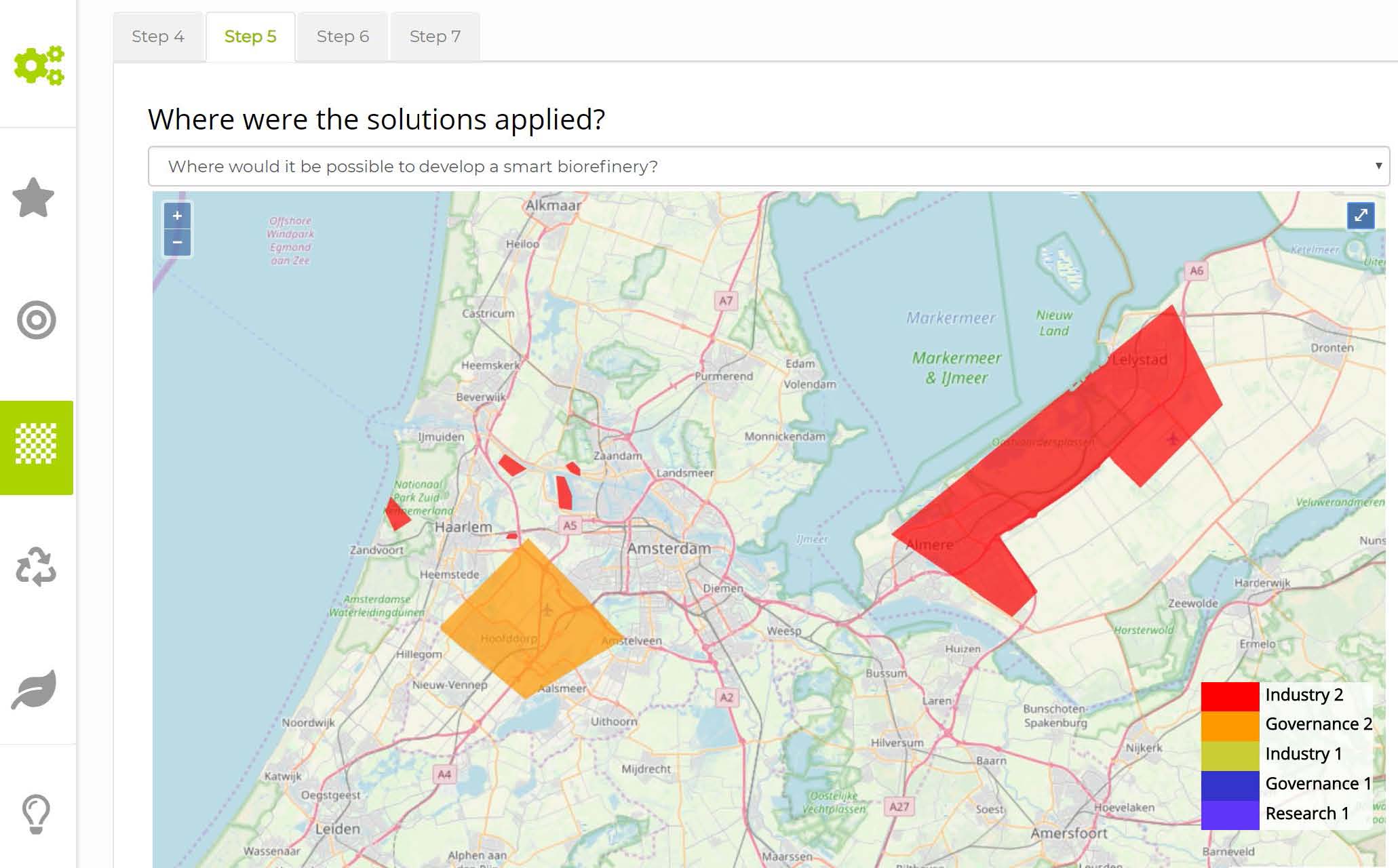
- Where were the solutions applied?
- Which actor groups are touched by the selected solutions? Which most often?
- Which stakeholders were chosen for implementing solutions?
- How much do the strategies modify the flows?
- Which strategy is able to meet which own target?
By leading through these questions, the GDSE helps to find common ground (and fields for further discussions) for a cooperative strategy approach of the workshop participants.
An in-built notepad functionality enables the workshop leaders to write down each conclusion right away during the workshop, well visible to all participants.
A more detailed description of the GDSE can be found here.